
How to Choose an Air Conditioner by Power (W, BTU, Frigorías)
When selecting an air conditioner, it is important to consider its power, measured in watts (W), British thermal units (BTU), and frigorías (Fr). These units help determine how effectively the device can cool or heat a space.
What Do These Units Mean?
- W (watts) – the international unit of power measurement. In air conditioners, both the consumed and cooling power are indicated.
- BTU (British Thermal Unit) – a British thermal unit. 1 BTU is the amount of energy required to heat 0.45 liters of water by 1°F.
- Frigorías (Fr) – used in Europe and Latin America. 1 Fr is approximately equal to 1 kcal/h.

Basic Calculation of Air Conditioner Power
The minimum power of the air conditioner is calculated using the following formula:
where:
- S — area of the room (m²),
- H — ceiling height (m),
- 40 — average heat release coefficient (W/m³).
However, this calculation requires adjustments considering additional factors.
Additional Factors Affecting Air Conditioner Power
Room Orientation
- If windows face the sunny side, the room heats up faster, so add:
- +15% if the room receives direct sunlight during the day.
- +20% if the room has panoramic windows or glass walls.
- No adjustments are needed for rooms on the shady side.
- If windows face the sunny side, the room heats up faster, so add:

Number of People in the Room
- Heat emitted by people also influences power selection:
- Passive individuals (sedentary work, resting) → +100 W per person.
- Active individuals (physical activity, sports) → +300 W per person.
Example: In an office with 5 employees, add 5 × 100 = 500 W to the total power.

- Heat emitted by people also influences power selection:
Electrical Appliances (Heat Sources)
- Any equipment emits heat, especially powerful devices. Average contributions to heat load:
- Computer, laptop → +200 W.
- TV, monitor → +150 W.
- Kitchen appliances (microwave, stove, refrigerator) → +500-1000 W.
- Lighting (total lamp power) → +10% of lamp power.
Example: In an office with 3 computers and one TV, add (3 × 200) + 150 = 750 W.
- Any equipment emits heat, especially powerful devices. Average contributions to heat load:
Ceiling Height Influence on Air Conditioner Selection
- How does ceiling height affect air conditioner power?
- Standard power calculations usually assume ceiling heights of 2.5–2.7 m. If the ceilings are higher, the room volume increases, requiring a more powerful air conditioner.
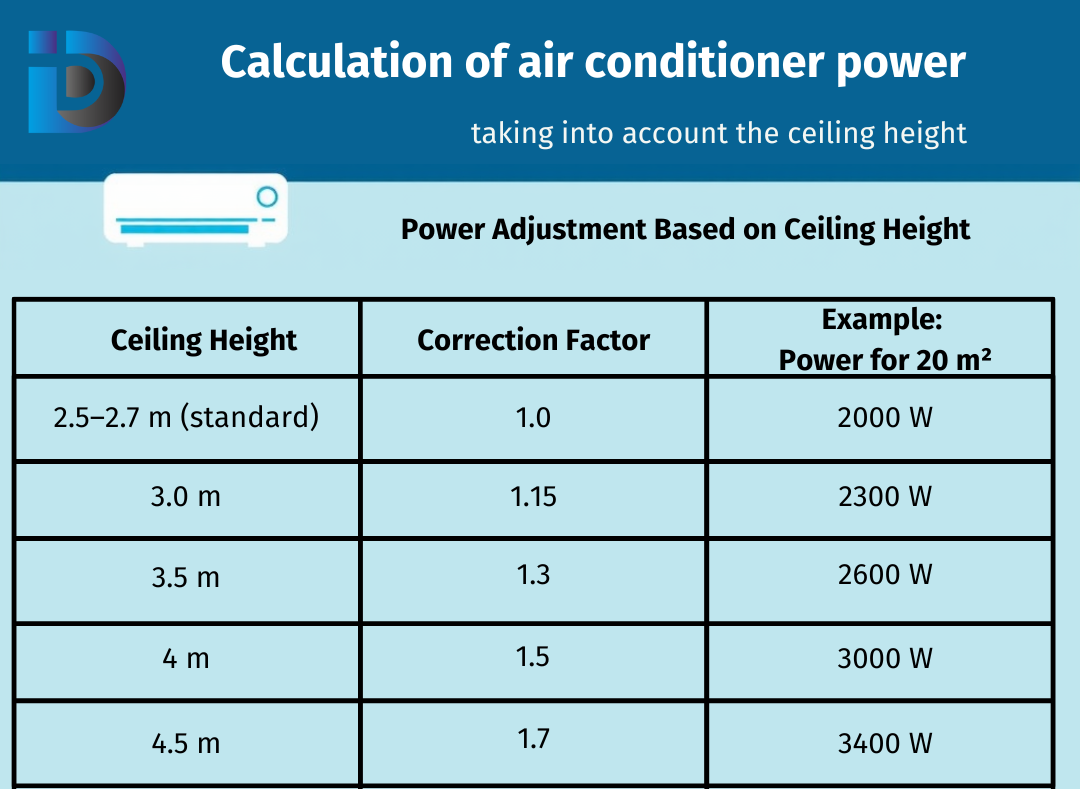
Power Adjustment Based on Ceiling Height
Use a correction factor for accurate power selection:
where:
- S — area of the room (m²),
- H — ceiling height (m),
- 40 — standard heat release coefficient (W/m³).
Power Adjustment Table Based on Ceiling Height
| Ceiling Height | Correction Factor | Example: Power for 20 m² |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5–2.7 m (standard) | 1.0 | 2000 W |
| 3.0 m | 1.15 | 2300 W |
| 3.5 m | 1.3 | 2600 W |
| 4.0 m | 1.5 | 3000 W |
| 4.5 m | 1.7 | 3400 W |
What to Do If Ceilings Are Higher Than 3 Meters?
- Calculate power based on volume (S × H).
- Use an air conditioner with higher power (considering the coefficient from the table).
- Consider installing multiple air conditioners (for even cooling distribution).
- Apply systems with enhanced air circulation (cassette, ducted models).
Adding this information will help users select an air conditioner considering ceiling heights.
Comparative Power Table for Air Conditioners
Here’s a table for air conditioners with various BTU/h ratings, with equivalent values in frigorías, kW, and suggested room areas.
- 1 BTU/h ≈ 0.252 Fr ≈ 0.293 W is used for calculations.
| BTU/h | Frigorías | kW | Area (m²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7000 | 1764 | 2.06 | 20-25 |
| 9000 | 2268 | 2.64 | 25-30 |
| 12000 | 3024 | 3.52 | 30-40 |
| 15000 | 3780 | 4.41 | 40-50 |
| 18000 | 4536 | 5.29 | 50-60 |
| 24000 | 6048 | 7.03 | 60-80 |
| 30000 | 7560 | 8.81 | 80-100 |
| 36000 | 9072 | 10.59 | 100-120 |
| 48000 | 12096 | 14.12 | 120-150 |
| 60000 | 15120 | 17.63 | 150-180 |
Notes:
- The area is an approximate estimate that may vary depending on operating conditions, insulation, number of people, electrical appliances, orientation, climate, etc.
For accurate air conditioner power selection, it is essential to consider not only the room area but also additional factors:
- The direction the windows face.
- The number of people and their activity level.
- Electrical appliances emitting heat.
Use the calculation formula and correction factors to choose the optimal air conditioner model and ensure a comfortable microclimate in the room!
Example Calculation of Air Conditioner Power
Suppose you need to select an air conditioner for a 30 m² room with a ceiling height of 2.8 m, which faces the sunny side, and has 2 people and 1 computer.
Basic power calculation:
Adjustment for sunny side (+15%)
Add heat from people (2 × 100 W)
Add computer (+200 W)
Conclusion: For such a room, an air conditioner with a power of 4200-4500 W (~15000 BTU), 3615-3875 frigorías is required.







Leave a Comment